
Lab's research plan
The LA Lab's team continuously and closely follows the developments related to LA research, which is reflected in our research plan. Our most current research endeavors are primarily related to learning design and design analytics, assessment analytics, developing predictive LA models, and the trustworthiness of LA and AI in education. However, our research plan is much broader, and includes a range of related topics.
Learning design describes the teaching and learning activities leading to the acquisition of intended learning outcomes. Design analytics help the development and upgrading of learning design that aligns with learning outcomes and student-centered, innovative pedagogies. Learning design and LA are interconnected: while sound learning design is essential for meaningful LA, insights from LA present a valuable basis for upgrading learning design.
LA provides an important input in the development and improvement of assessment programs, including their validity and reliability. Different kinds of data can used for analyses, like assessment data and trace data from LMSs, but also multimodal data.
Trustworthiness of LA, closely related to the trustworthiness of AI, has been gaining more focus in the LA community lately. The research focuses on various aspects, such as privacy and data protection, agency, data quality, algorithms, infrastructure, transparency, and other.
Predictive LA uses past and present data patterns to predict outcomes in the future, usually using machine learning algorithms. It uses different kinds of data, including students' academic data, as well as behavioral, demographic and other data.
Appropriate visualizations could make a significant contribution to understanding the large amounts of educational data. Statistical, filtering, and mining tools should be designed in a way that can help learners, teachers, and institutions to achieve their analytics objectives. Educational data mining tools should be designed for non-expert users in data mining.
Investigate how LA could impact learning and how this could be evaluated. Further research is required to investigate effective mixed-method evaluation approaches that do focus on the usability of the LA tool, but also on aim at measuring its impact on learning.
What sort of indicators and metrics are helpful in each learning situation. LA tools should support an exploratory, real-time user experience. From a technical perspective, templates and rule engines can be used to achieve goal-oriented LA for improved personalized learning.
Our research bridges learning analytics theory and practice, exploring responsible uses of analytics, AI and data-driven methods to support learning design, assessment, personalized learning and meaningful educational impact.

About learning analytics
Learning Analytics is an emerging interdisciplinary field that integrates education, data science and technology to better understand and enhance learning. Through the systematic collection and analysis of data generated during learning, LA offers valuable insights for students, teachers and institutions, enabling evidence-based improvements in learning design, assessment and educational decision-making. The concepts and definitions presented here are grounded in established research in the field (see References).
Learning analytics (LA) is a relatively new, but already propulsive and influential interdisciplinary field (Divjak & Maretić, 2017) bringing together research and practice in education, data science and psychology (Tsai et al., 2018). According to the definition adopted by the Society for LA Research (SOLAR), LA is “the measurement, collection, analysis and reporting of data about learners and their contexts, for purposes of understanding and optimising learning and the environments in which it occurs” (SOLAR, n. d.). As such, LA provides valuable insights for teachers and students, but also for instructional designers, institutional leaders and administration, and researchers.
While evidence has been used to enhance teaching and learning for many years, LA brings novelty by making use of new digital data on students’ learning activity and analysis techniques from data science and AI (SOLAR, n. d.). LA analyses data produced predominantly (though not exclusively) in students’ interactions with ICT, primarily with learning management systems (LMS) (e.g. Moodle) (Divjak & Maretić, 2017). New developments are related to using multimodal datafrom different sources, including data from digital, but also physical environments (Yan et al., 2022). LA are increasingly used to support sound learning design (Rienties et al., 2017), in particular in ensuring constructive alignment between learning outcomes, teaching and learning activities and assessment (Divjak et al., 2023b). LA turns data into “insights, decisions, and actions to improve learning and teaching” (Chatti et al., 2020). It is applicable in formal, but also non-formal education, and informal learning (Divjak & Maretić, 2017), including industrial training.
LA provides insights into student's learning processes and gaps in understanding. This can help teachers recognise weaknesses in learning activities and challenging topics, as well as provide constructive feedback that can enhance students’ further learning (Gašević et al., 2015). As for students, LA plays a significant role in fostering self-regulated learning (Schumacher & Ifenthaler, 2018) as an active process in which students set their learning goals and then “monitor, regulate, and control their cognition, motivation, and behaviour” (Pintrich, 2000, p. 453). An area of particular research interest has recently been related to assessment analytics (Nguyen et al., 2017; Divjak & Maretić, 2017) In higher education, analytics often aims at early identification of students at risk, as a basis for interventions aimed at maximizing student retention, and enhancing the quality of student's learning experiences (Susnjak et al., 2022).
Some of the key goals of LA include providing students with personalised and timely feedback on their learning, and supporting awareness through self-reflection; supporting the quality of learning and teaching with evidence on the success of innovations; supporting students in development of lifelong learning skills and strategies, as well as skills like critical thinking, collaboration, creativity, communication (SOLAR, n. d.).
LA can have different levels of complexity, supporting informed decision-making by providing several layers of insights ( Susnjak et al., 2022; SOLAR, n. d.) :
- descriptive analytics provides basic information about trends and current status
- diagnostic analytics looks into why something happened
- predictive analytics provides forecasts and estimates future outcomes (based on past and current patterns)
- prescriptive analytics produces tailored recommendations and suggestions for behavioural changes which could lead to positive outcomes.
Publications
Our research includes an extensive portfolio of publications with significant contributions to the field.
Here we present a selection of our most recent work.
Navigating Strategic Challenges in Education in the Post-pandemic AI Era
Divjak, B. (2024)
Research context: TRUELA project
Research context: TRUELA project
Reviewing Assessment in Online and Blended Flipped Classroom
Divjak, B., Rienties, B., Svetec, B., Vondra, P., Žižak, M. (2024)
Research context: LA Lab
Research context: LA Lab
How can valid and reliable automatic formative assessment predict the acquisition of learning outcomes?
Divjak, B., Svetec, B., Horvat, D. (2024).
Research context: LA Lab
Research context: LA Lab
Assessment validity and learning analytics as prerequisites for ensuring student-centred learning design
Divjak, B., Svetec, B., Horvat, D., Kadoić, N. (2023).
Research context: LA Lab
Research context: LA Lab
Learning analytics dashboards: What do students actually ask for?
Divjak, B., Svetec, B., Horvat, D. (2023).
Research context: LA Lab
Research context: LA Lab
Posters
A strong international presence through conference posters showcasing research, tools and innovations
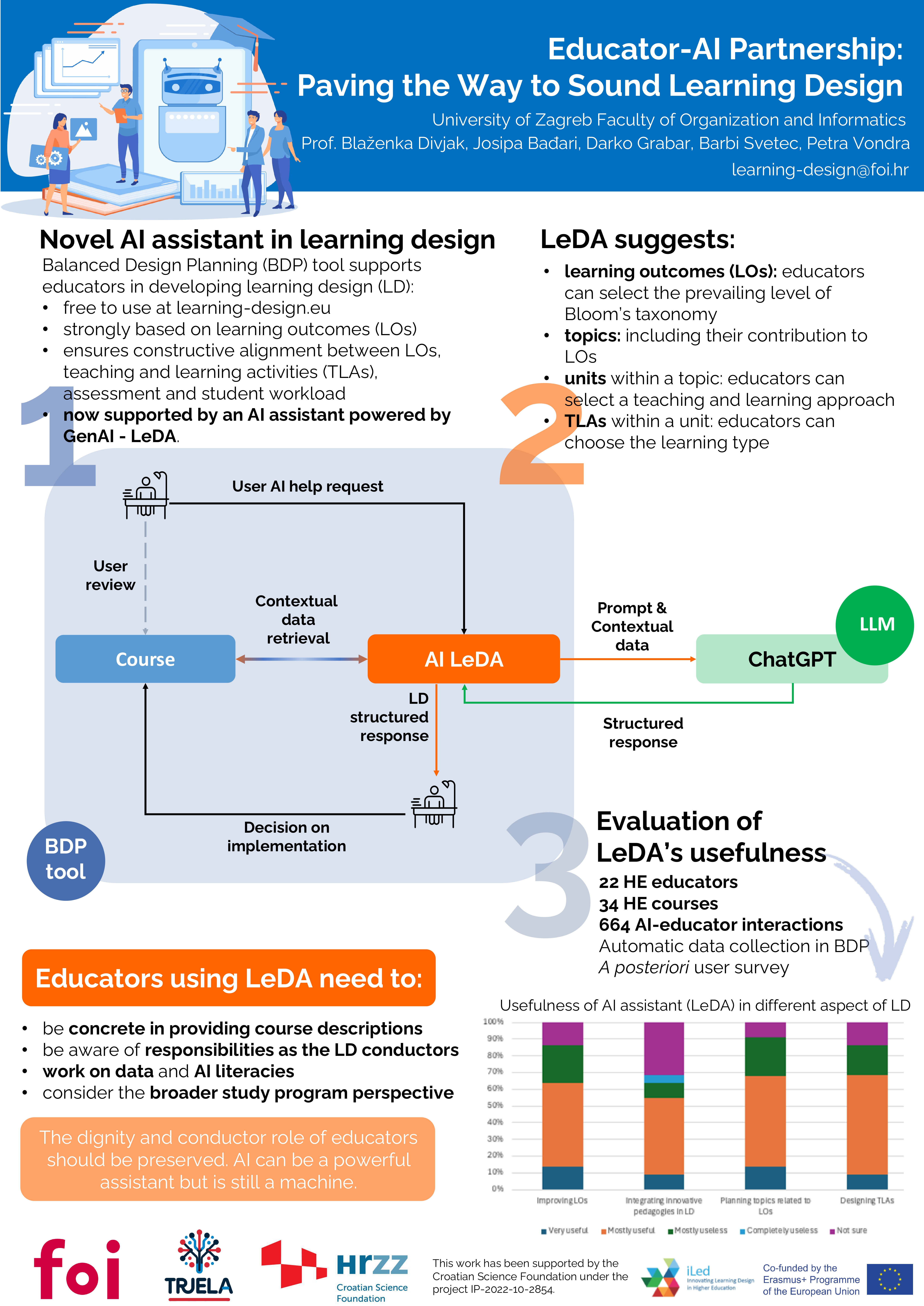
Educator-AI Partnership: Paving the Way to Sound Learning Design
LAK 2025
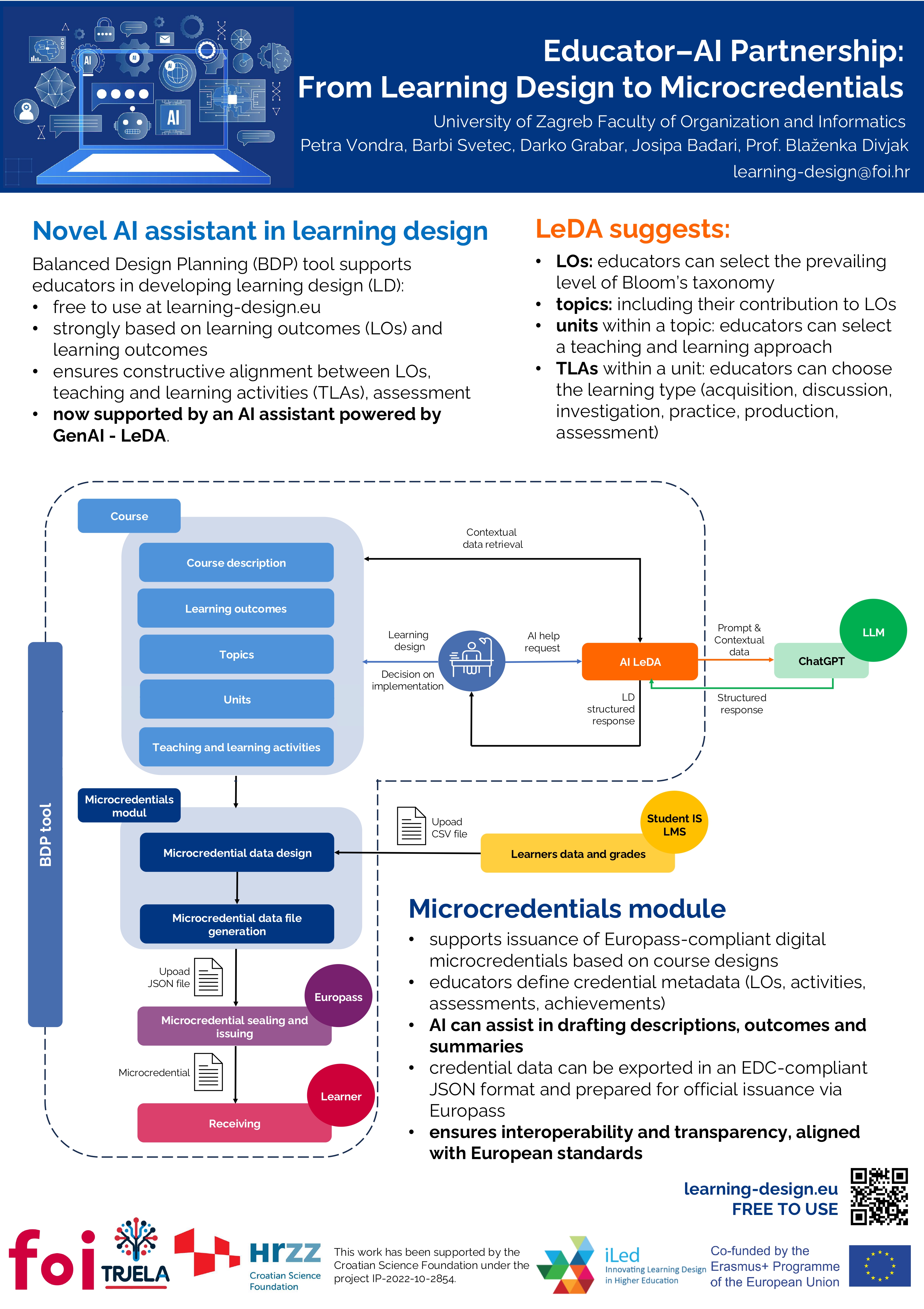
Educator-AI Partnership: From Learning Design to Microcredentials
CECIIS 2025
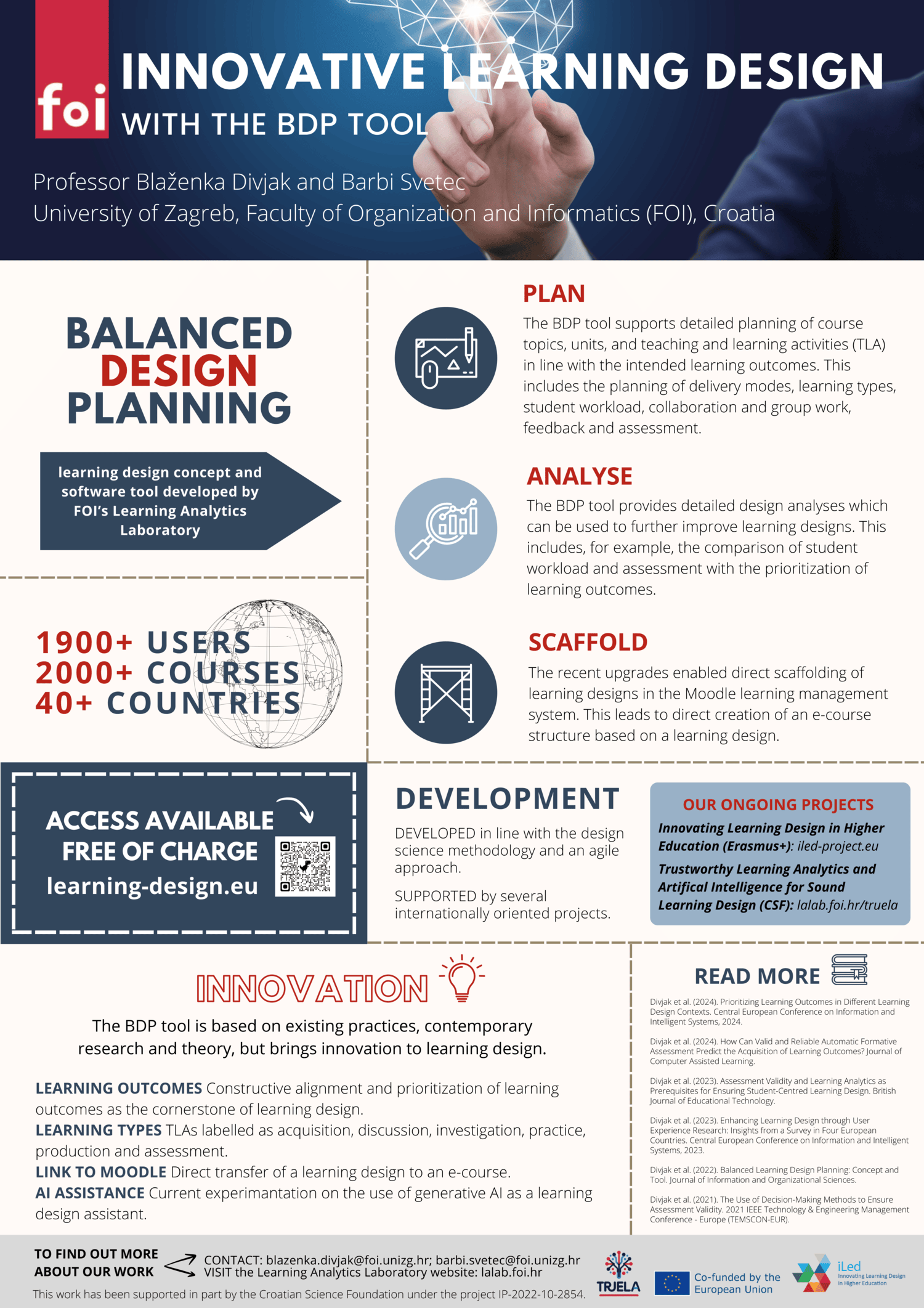
Innovative Learning Design with the BDP Tool
The 4th International Educational Conference, 2024

Enhancing Teaching and Leanring Through Balanced Learning Design
CECIIS 2024
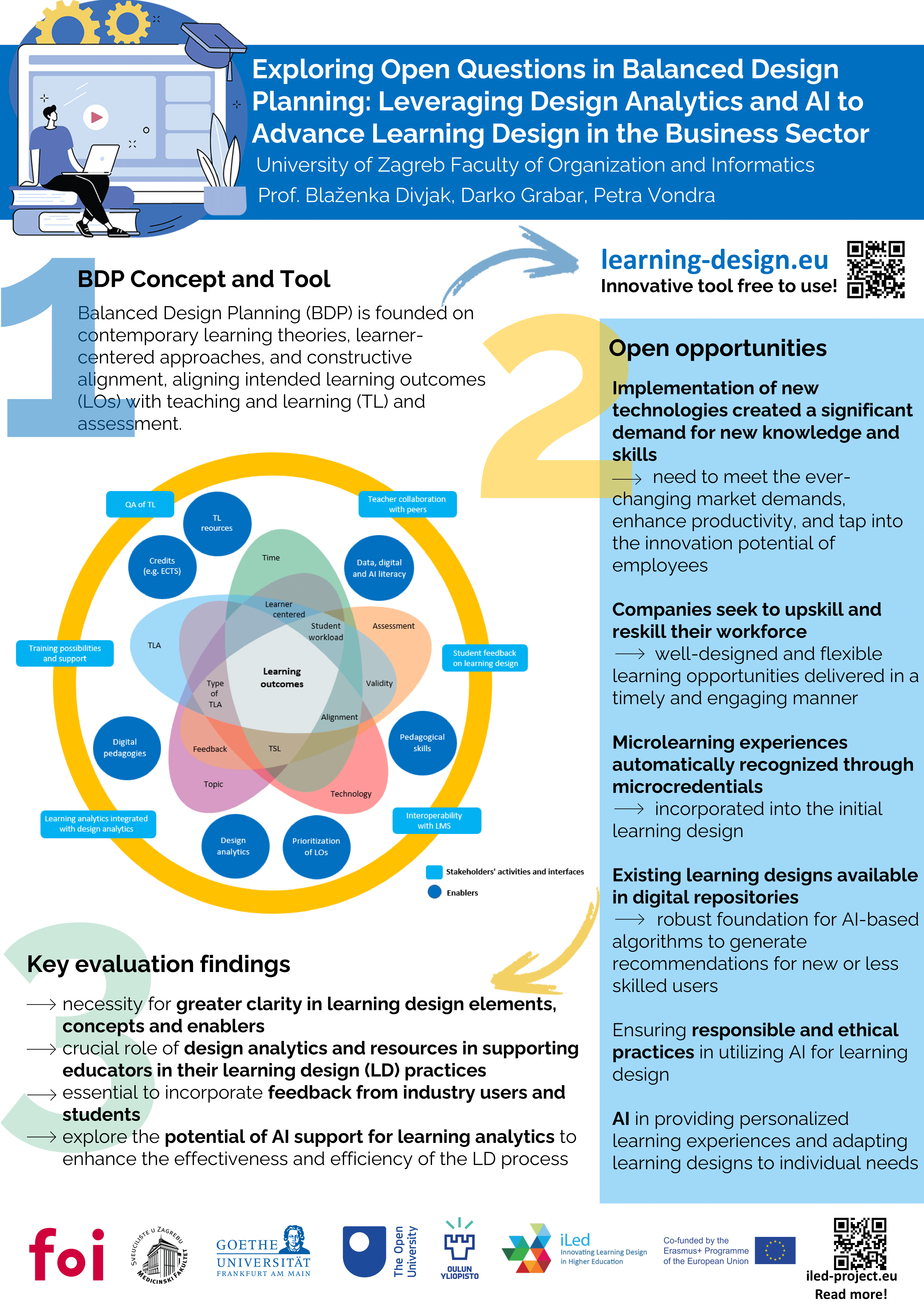
Exploring Open Questions in Balanced Design Planning: Leveraging Design Analytics and AI to Advance Leanring Design in the Business Sector
CECIIS 2023
